What is Cloud Technology? What Does It Do?
Cloud services are the generic name given to online services, which gained popularity with the discovery of certain information opportunities, have been a part of our life for a long time, and are generally used by large companies to serve individual users on the Internet within certain rules, facilitating our daily life and benefiting us in many ways. Before answering the question about the application and operation of cloud technologies, let's take a look at their history.
History of Cloud Technology
Although the foundations of the technology referred to as cloud services can be based on the Internet, and even the first network studies (ARPANET, USENET, etc.), we will consider cluster computing systems as a starting point in this article. These systems typically were used by academic, commercial, or government agencies that required high computing power. The spread of the Internet and the reduction of network costs have led to the emergence of grid computing systems with a distributed architecture (although juicy grilled chicken meat may come to mind, that is not the kind of grid we are talking about), which moved cluster computing one step forward. Recognizing the cost, performance, and resilience benefits of this new distributed architecture, the information community and leading companies quickly enabled almost all IT services to evolve and started offering cloud computing services. There are thousands of cloud services provided by leading cloud computing companies (Amazon, Microsoft, Google, AliBaba, etc.) today.
As cloud computing reaches its current level, a fog computing framework intended to enable more efficient use of distributed architecture and additional latency optimization on the part of clients, and a dew computing framework that connects client devices to the cloud were created.
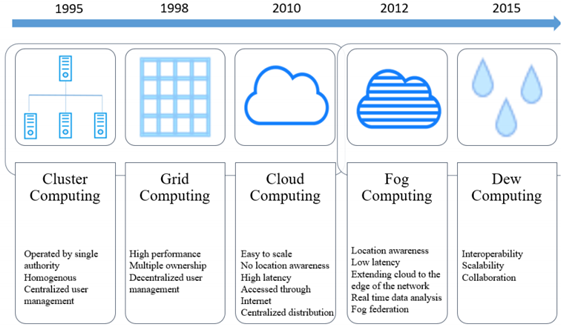
Types of Cloud Technology
Many of the applications we use today benefit from cloud services. However, the level of utilization of these cloud services, or in other words, the speed of access to the cloud, can vary. Cloud services are usually divided into three main groups according to this ratio. These classifications are usually made in proportion to the distribution of responsibilities.
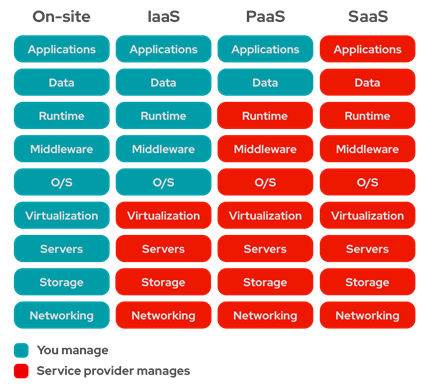
Getting to Know the Building Blocks of Cloud Technology
Before moving on to the official definition of the above mentioned classifications, we can draw an analogy with lahmajun (a dish similar to thin crust pizza baked with minced meat and vegetables - translator's note). For example, while making lahmajun at home is On-Site informatics, baking lahmajun in the oven from prepared ingredients can be considered IaaS, baking even the dough ourselves in our oven is PaaS, and the situation when we choose to visit a restaurant can be described as SaaS. Now it is the time for the official definition;
On-Site: It is the situation where all equipment and services are provided by the company using its resources. For example, military applications are usually created on-site for security reasons. Although the security of cloud systems can often be close to the military level, most of the regular companies are reluctant to impose such military requirements due to the high-security standards and massive costs involved.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): It is the type of service where the applications and the sub-software needed for the applications to run are managed by the company itself, but the hardware and network needs are managed by the cloud service provider. For example, virtual machine service, cloud storage (hardware level) service, virtual machine backup service, virtual private network services can be provided this way.
PaaS (Platform as a Service): It is the type of service where all the infrastructure services needed by the applications are provided by the cloud provider, but the application itself is prepared by the company. For example, the services provided in an architectural design where your application receives all network, security, storage services, database, application server, and cloud artificial intelligence services can be described as PaaS.
SaaS (Software as a Service): At this last level, companies are now users of these services instead of producing software or technology. The good part of this is that it does not require any infrastructure and development costs other than SaaS service costs. If the technological applications, which your business demands, can be met with standard products that are not specific to you, this may be the ideal solution. However, it may not be easy to make technological moves and achieve innovations that will make a difference. Examples of SaaS are Office365, Salesforce, or DropBox. As you have noticed, SaaS applications are branded and multi-tenancy applications that are the most familiar to us.
Advantages of Cloud Technologies
So why do many established companies want to move their applications to the cloud? While you have already invested millions of dollars, of course, the reason for switching to the cloud is not just that it is cool. Thanks to cloud computing, businesses aim to have many advantages. The most important of these are;
Cost: The applications that many companies use to fulfill their daily work are actually applications that many other companies use as well. As in the examples of Office365 or Salesforce we gave in the previous topic, it would be a much lower cost solution to "rent" these applications rather than rewrite them.
Scalability: Today, many successful startup companies grow rapidly following the establishment phase and address the increase in technological requirements brought by this growth with the scalability feature offered by cloud services. Even these scales can be daily or even hourly. For example, a digital broadcasting organization can automatically increase infrastructure costs when offering popular content and automatically return it to its standard level later.
Security: So, is cloud technology safe? In the old order where there was no cloud computing, every firm was responsible for its safety. Although this is a bearable cost for large companies, the companies with relatively low technology investments trying to cope with limited security knowledge and experience often face many security vulnerabilities. Thanks to cloud computing, every organization can get its basic security needs with the most accurate configuration guarantee and become able to offer additional security services and services more reliably in line with their demands.
Sustainability: Many cloud providers serve in a wide variety of geographic locations. The reason for this is, if there is a problem in one of these spots, they want to set up an infrastructure that can offer their services from other places almost without interruption. This way, a bank can serve its customers from different sites shall a hardware failure or a natural disaster appear in the area where the infrastructure is located.
Apart from these features, many other pleasant characteristics, such as performance, efficiency, and variety, can be added to the list. However, and perhaps most importantly, we can say that the development of cloud services, the Internet, and distributed systems, provides an infrastructure that enables businesses to do everything they do on a global scale. So going to the cloud can offer you a world without borders.
References:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/overview/what-is-cloud-computing/
https://zegetech.com/blog/2018/11/12/cloud-cloud-computing.html
https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/cloud-computing/iaas-vs-paas-vs-saas
https://www.daaam.info/Downloads/Pdfs/proceedings/proceedings_2018/144.pdf











In the magical world of computers, which I entered 25 years ago as a professional, I had the opportunity to work on various positions in different academic and business institutions. Since becoming a member of the Borusan family in 2018, I have been moving towards the difficult but enjoyable way of digitalization. When I get out of the digital world, I usually enjoy spending time with my family and traveling.